Introduction to Forensics

- The main goal of digital forensics is to answer the big five W’s, regarding any digital incidents.
1. What
2. Where
3. When
4. Who
5. How

- Digital Evidence Life Cycle
1. Acquisition
2. Analysis
3. Presenation

Source of Digital Evidence
Active Data
Archive or Backup Data
Hidden Data

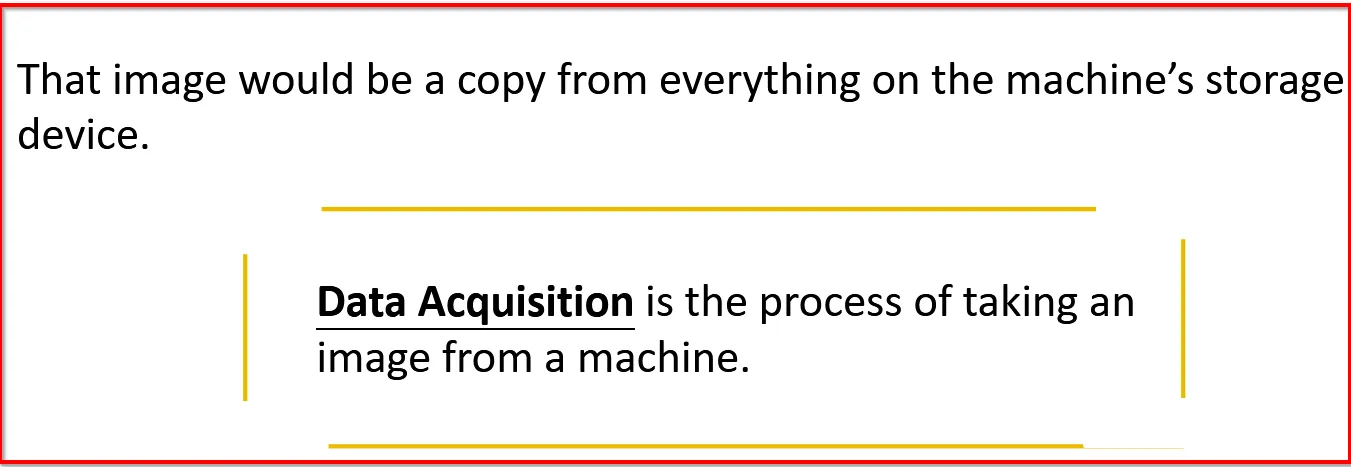
DATA ACQUISITION
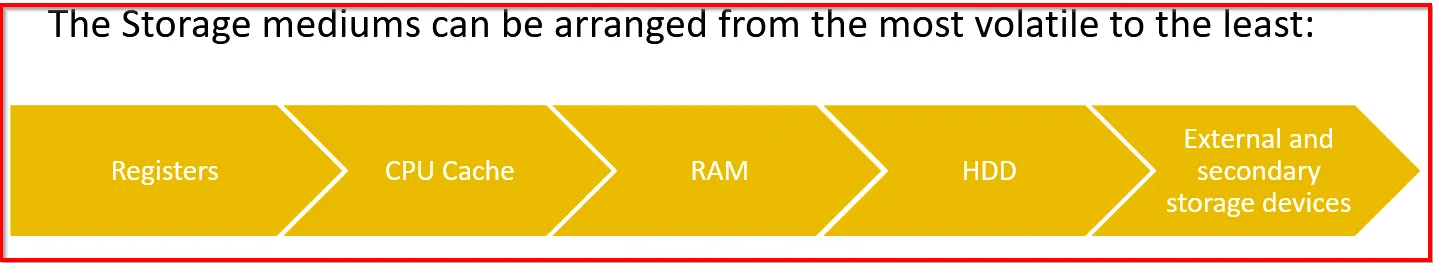
Order of Volatility
Storage Formats:
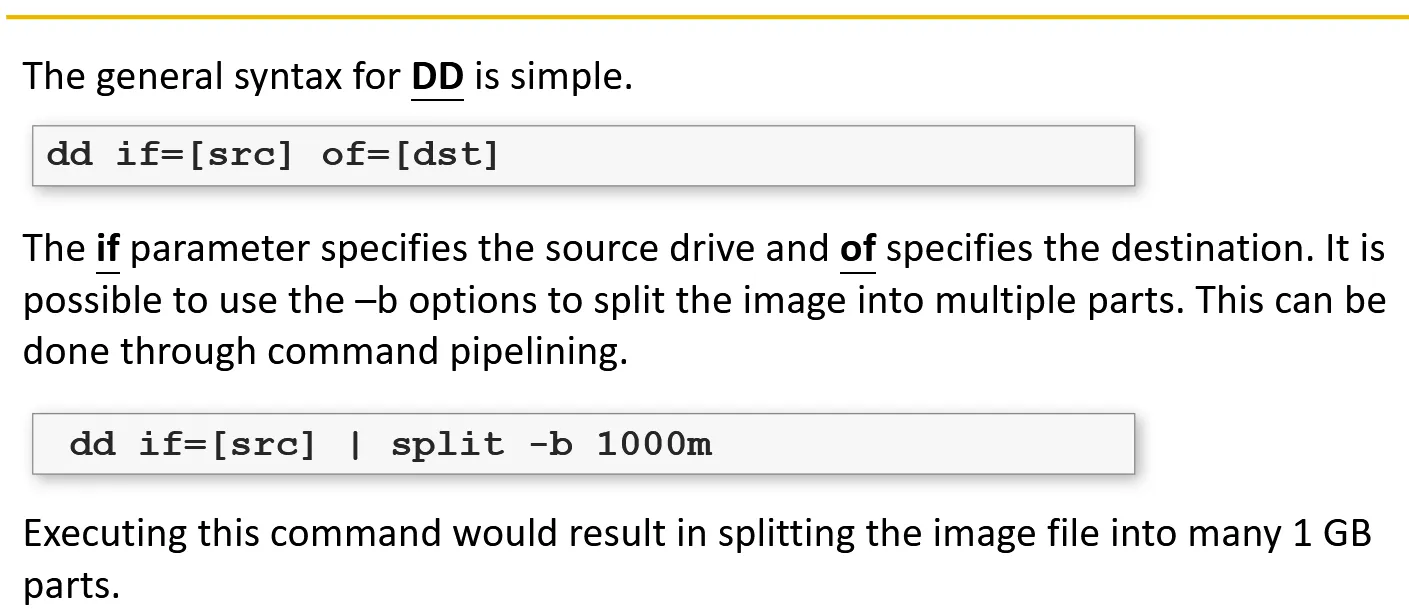
- One popular tool to image a disc in a raw format is DD tool available for both Linux and Windows(with RawWrite Studio)
-
DD allows investigator to image a disk in raw format and split the single file into multiple files.
Mostly used in linux:
-
(AFF) Advanced Forensics Format :- It is an open image format developed by Basis Technology. Alongside compression, which helps save disk space, and integrity checks most AFF tools allows the investigator to add customary fields. It also allows the investigator to embed metadata within or on a separate file.
-
Data Acquisition vs Copy:
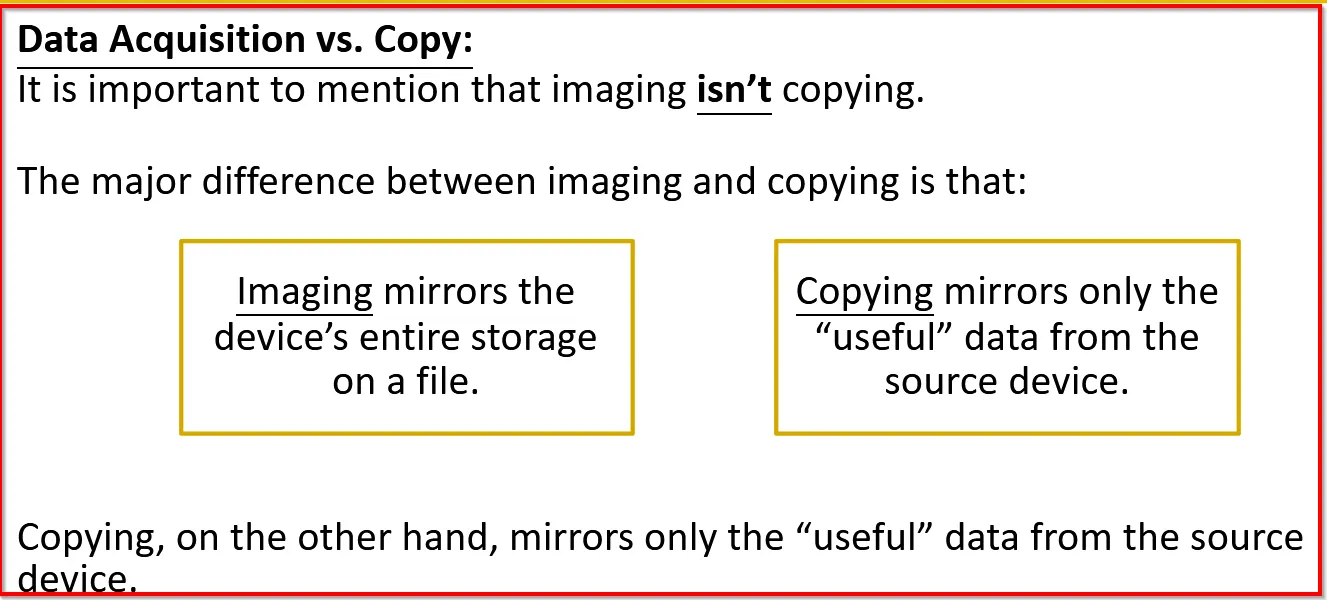
Eg: If disk have 60% capacity and remaining 40% of rubbish (deleted files or random bytes), then imaging will occupy the both used and unused parts. But copying will only mirror the 60% of the memory:
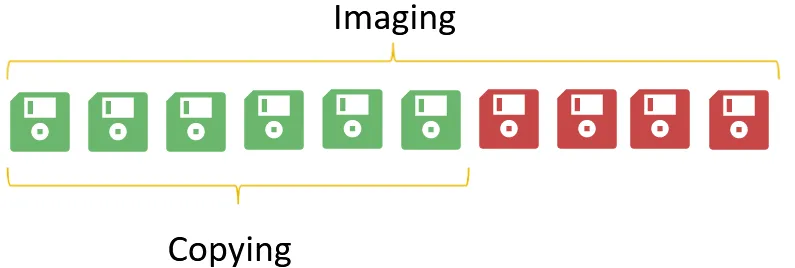
Acquisition Methods
- First way is : from disk drive to image file (Imaging)
- Second way is: from disk drive to disk drive (Cloning)
Sparse Acquisition:- It is when the investigator doesn’t mirror all the disk content. This acquisition is mostly used when it might take hours to forensically image or clone the drive.
Live Data Acquisition:
Collecting the data while the machine is running.
Tools
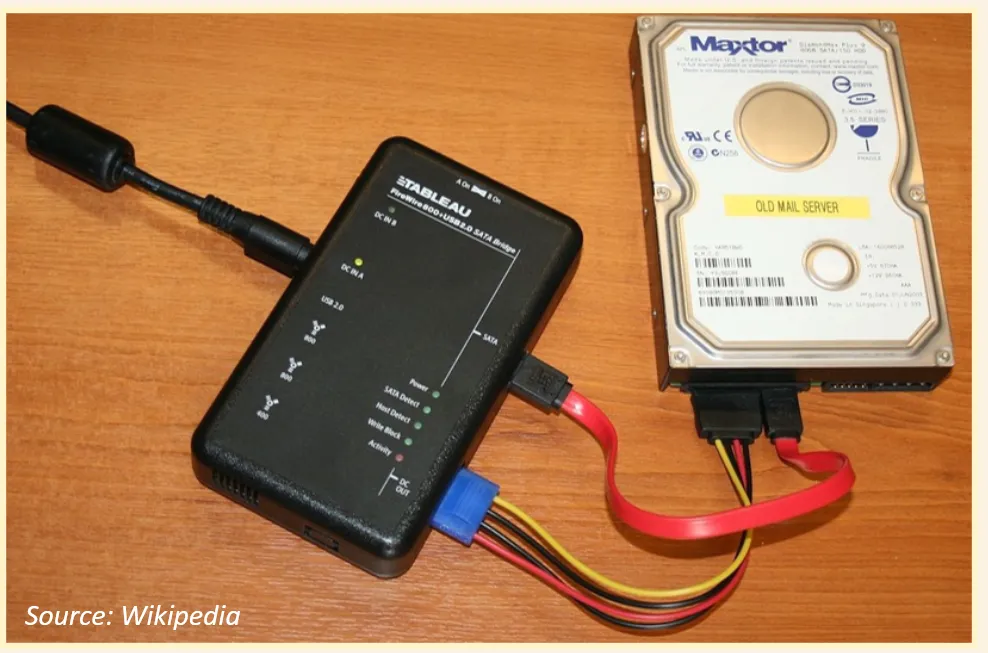
Write Blockers:- These tools allow the investigator to perform data acquisition by eliminating the chance of damage or altering the disk contents. It works by blocking the hard disk from writing and this is done by filtering the write commands and preventing it from being executed.

Bootable Disks:- Contains fully functioning, bootable OS. This allows the investigator to launch an OS on suspect’s machine without touching and modifying main disk.
Non-writable USB:- Microsoft introduced a USB-write blocking feature (first in Windows XP). It can be activated from Registry and will prevent the write access on the USB devices preserving the evidence integrity. Note: This is useful when we are creating an image for USB devices.
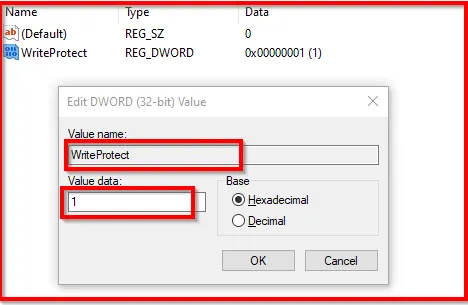
This can be created using regedit:
- Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control
- Create a new key StorageDevicePoilcies
- Create new DWORD(32)Value (named: WriteProtect) key value set to 1
FTK(Forensic Toolkit) Imager:- It is the most famous tools in forensics world. This tool allows to acquire various types of storage devices and store them in different formats for analysis.
Live Response Tools:- Live Response collection is a vary handy framework from Bambiraptor, which can collect various and useful information from machine
Memory Forensics Tools:
Volatility Framework:- It is a completely collection of tools, implemented in Python.
Other Forensic Tools
Bulk Extractor:- Computer forensics tool, that scans disk image, file or a directory of files and extracts useful information without parsing the file system or file system structures.
